Kubernetes
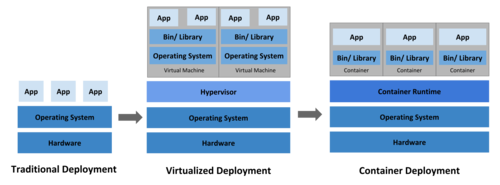
Kubernetes is an open source system for managing containerized applications across multiple hosts. It provides basic mechanisms for deployment, maintenance, and scaling of applications.
Contents
Kubernetes Components[edit | edit source]
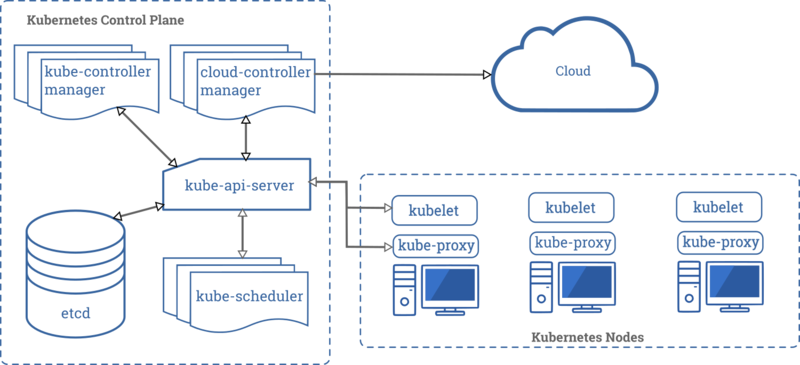
When you deploy Kubernetes, you get a cluster. The cluster is composed of many components. Here are brief details on some of them.
Kube-apiserver[edit | edit source]
The API server is the front end for the Kubernetes control plane.
The main implementation of a Kubernetes API server is kube-apiserver. kube-apiserver is designed to scale horizontally—that is, it scales by deploying more instances. You can run several instances of kube-apiserver and balance traffic between those instances.
etcd[edit | edit source]
Consistent and highly-available key value store. Used for backing store for all cluster data. https://etcd.io/docs/
Kube-controller-manager[edit | edit source]
Kubeadm[edit | edit source]
Kubeadm is a component of Kubernetes.
- Kubeadm is a tool built to provide best-practice "fast paths" for creating Kubernetes clusters. It performs the actions necessary to get a minimum viable, secure cluster up and running in a user friendly way. Kubeadm's scope is limited to the local node filesystem and the Kubernetes API, and it is intended to be a composable building block of higher level tools.
Kubectl[edit | edit source]
Kube-proxy[edit | edit source]
Kube-scheduler[edit | edit source]
Control plane component that watches for newly created Pods with no assigned node , and selects a node for them to run on.
Factors taken into account for scheduling decisions include: individual and collective resource requirements, hardware/software/policy constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload interference, and deadlines.