Kubernetes: Difference between revisions
draft |
Initial version complete |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=== etcd === | === etcd === | ||
Consistent and highly-available key value store. Used for backing store for all cluster data. https://etcd.io/docs/ | Consistent and highly-available key value store. Used for backing store for all cluster data. https://etcd.io/docs/ | ||
=== Kube-scheduler === | |||
Control plane component that watches for newly created Pods with no assigned node , and selects a node for them to run on. | |||
Factors taken into account for scheduling decisions include: individual and collective resource requirements, hardware/software/policy constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload interference, and deadlines. | |||
=== Kube-controller-manager === | === Kube-controller-manager === | ||
Control Plane component that runs controller processes; including Node controller, Replication controller, Endpoints controller, Service Account and Token controllers. | |||
=== Cloud-controller-manager === | |||
A Kubernetes control plane component that embeds cloud-specific control logic. The cloud controller manager lets you link your cluster into your cloud provider's API, and separates out the components that interact with that cloud platform from components that just interact with your cluster. | |||
== | == Node Components == | ||
Node components run on every node, maintaining running pods and providing the Kubernetes runtime environment. | |||
=== | === Kubelet === | ||
An agent that runs on each node in the cluster. It makes sure that containers are running in a Pod . | |||
=== Kube-proxy === | === Kube-proxy === | ||
kube-proxy is a network proxy that runs on each node in your cluster, implementing part of the Kubernetes Service concept. | |||
=== | === Container runtime === | ||
The container runtime is the software that is responsible for running containers. Docker by default, it can also be CRI-O or possibly other implementations of the Container Runtime Interface. | |||
== Addons == | |||
You probably need at least the DNS and Web UI [https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ addons]. | |||
== Tools == | |||
=== Kubectl === | |||
The [https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/ <code>kubectl</code>] command line tool lets you control Kubernetes clusters. | |||
=== Kubeadm === | |||
[https://github.com/kubernetes/kubeadm Kubeadm] is a [https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/cmd/kubeadm component of Kubernetes]. | |||
: Kubeadm is a tool built to provide best-practice "fast paths" for creating Kubernetes clusters. It performs the actions necessary to get a minimum viable, secure cluster up and running in a user friendly way. Kubeadm's scope is limited to the local node filesystem and the Kubernetes API, and it is intended to be a composable building block of higher level tools. | |||
[[Category:Virtualization]] | [[Category:Virtualization]] | ||
Revision as of 18:31, 4 August 2020
Kubernetes is an open source system for managing containerized applications across multiple hosts. It provides basic mechanisms for deployment, maintenance, and scaling of applications.
Kubernetes Components[edit]
When you deploy Kubernetes, you get a cluster. The cluster is composed of many components. Here are brief details on some of them.
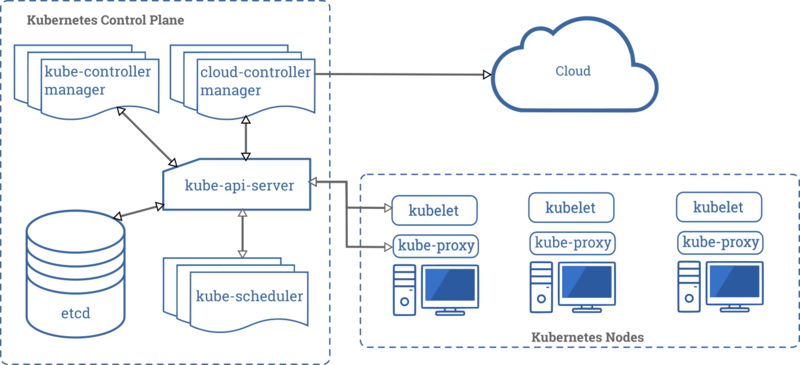
Kube-apiserver[edit]
The API server is the front end for the Kubernetes control plane.
The main implementation of a Kubernetes API server is kube-apiserver. kube-apiserver is designed to scale horizontally—that is, it scales by deploying more instances. You can run several instances of kube-apiserver and balance traffic between those instances.
etcd[edit]
Consistent and highly-available key value store. Used for backing store for all cluster data. https://etcd.io/docs/
Kube-scheduler[edit]
Control plane component that watches for newly created Pods with no assigned node , and selects a node for them to run on.
Factors taken into account for scheduling decisions include: individual and collective resource requirements, hardware/software/policy constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload interference, and deadlines.
Kube-controller-manager[edit]
Control Plane component that runs controller processes; including Node controller, Replication controller, Endpoints controller, Service Account and Token controllers.
Cloud-controller-manager[edit]
A Kubernetes control plane component that embeds cloud-specific control logic. The cloud controller manager lets you link your cluster into your cloud provider's API, and separates out the components that interact with that cloud platform from components that just interact with your cluster.
Node Components[edit]
Node components run on every node, maintaining running pods and providing the Kubernetes runtime environment.
Kubelet[edit]
An agent that runs on each node in the cluster. It makes sure that containers are running in a Pod .
Kube-proxy[edit]
kube-proxy is a network proxy that runs on each node in your cluster, implementing part of the Kubernetes Service concept.
Container runtime[edit]
The container runtime is the software that is responsible for running containers. Docker by default, it can also be CRI-O or possibly other implementations of the Container Runtime Interface.
Addons[edit]
You probably need at least the DNS and Web UI addons.
Tools[edit]
Kubectl[edit]
The kubectl command line tool lets you control Kubernetes clusters.
Kubeadm[edit]
Kubeadm is a component of Kubernetes.
- Kubeadm is a tool built to provide best-practice "fast paths" for creating Kubernetes clusters. It performs the actions necessary to get a minimum viable, secure cluster up and running in a user friendly way. Kubeadm's scope is limited to the local node filesystem and the Kubernetes API, and it is intended to be a composable building block of higher level tools.