Difference between revisions of "Semantic MediaWiki/SMWCon2023"
(extracted from parent page) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 12:02, 22 December 2023
The 3-day program was fantastic!
One major announcement is that through Open Collective individuals and organizations can donate money to the Semantic MediaWiki project.
Contents
Day One[edit | edit source]
Day Two[edit | edit source]
Canasta[edit | edit source]
Canasta is a production grade distribution of MediaWiki developed by an informal consortium of the leading wiki hosters: WikiWorks, WikiTeq and MyWikis. It is also used / developed by the United States Space Force (USSF)
- video
- default content packages
- new wikifarm support
Digital Accessibility[edit | edit source]
Accessibility is extremely important, so do it everywhere all the time. See the A11Y checklist for a generic reference providing a quick implementation of WCAG
Specific to MediaWiki, see
- Accessibility as a design principle
- mw:Accessibility guide for developers and
- mw:Wikimedia Quality and Test Engineering Team/Playbooks/Accessibility,
- the Accessibility workboard in Phabricator or the
- full list of Open bugs and feature requests related to the accessibility in MediaWiki and other Wikimedia software
From the conference, here's the 5 minute call to action
Major changes on interfaces of MediaWiki RDBMS library[edit | edit source]
https://www.mediawiki.org/wiki/Manual:Database_access
This interesting example of Python3 code[1] uses antlr, php lexer and php parser to clean up deprecated Database::select() calls in PHP codebases
Day Three[edit | edit source]
Open Semantic Lab[edit | edit source]
Open Semantic Lab starts with the premise that Ontologies[2] are key to standardize everything... but tools are needed to make ontologies applicable in everyday research. The OSL is the holistic and community driven platform to fulfill this roll... and links people (knowledge), machines (data) and algorithms (AI) equally.
Since last year, the project has been completely based on the industry standards of JSON-SCHEMA and JSON-LD, enabling new applications quickly with easy integration to any third party software. Experimental support has been added to achieve Python triggered workflows through REST APIs and LocalGPT Q&A + search assistance.
The whole subject is quite advanced, so it can be hard to wrap your head around it. A good way to understand the power of the Open Semantic Lab system is to look at an example use case where it was put into practice[3]. At https://kiprobatt.de/wiki, they illustrate Intelligent battery cell manufacturing. The diagramming capabilities of the system are impressive - showing interactive (clickable) node graphs plus Draw.io integration. The underlying software application is not for the faint-of-heart. Checking the Special:Version page shows an extensive list of complex MediaWiki and Semantic MediaWiki extensions. The latest version's technology stack is represented here.
See also: https://opensemantic.world/ - a reference deployment of the OpenSemanticWorld packages. Here is a brief explanation of the key differences from 'vanilla' Semantic MediaWiki[4]. You can see at Special:Version, the extensions and software components.
Task tracking[edit | edit source]
HalloWelt! combines four extensions they created to make useful task tracking in (Semantic) MediaWiki
- Extension:SimpleTasks Tasks are checklist items that can be checked on or off to indicate if the task is open or completed.
- Extension:Checklists Make lists of checkboxes.
- Extension:DateTimeTools Provides date tools in VisualEditor.
- Extension:AtMentions Easily mention a user, with notification
Miriam Schlindwein presented how it's possible to create tasks, assign them to someone, add due dates and how they can be controlled
Realtime integrations with GitLab[edit | edit source]
Natural Language Queries to Wikidata: A Naïve Prototype[edit | edit source]
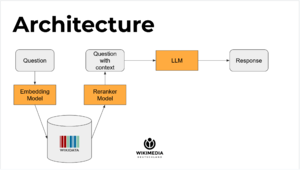
Robert Timms - Sr. Software Engineer Wikibase Suite, Wikimedia Deutschland gave a talk (code slides try it) about querying Wikibase with an LLM. Slides 9-22 go from the application architecture to the 'tada' moment.
Not the goal of the talk, but he revealed some of the key drawbacks of using "AI" in the first place:
- Outdated information
- Prone to hallucinations
- No sources (AI doesn't tell you how or why it claims to be authoritative.)
This is supposed to be addressed in part by using the RAG technique.
| The 'gpt' in ChatGPT stands for "Generative Pre-trained Transformer" - or a fancy way to say "guess". The artificial intelligence of large language model GPTs guess what you would say next based on the prompt given and the dataset they are trained on. In OpenAI's own words: "Generative AI models formulate responses by matching patterns or words, while RAG systems retrieve data based on similarity of meaning or semantic searches." |
Fixing Wikidata[edit | edit source]
Yaron Koren gave a great presentation (slides) called Enhanced Wikibase on how Wikibase (and therefore Wikidata) are missing features. He showed how he implemented these missing features in a series of developments. One is showcased at Wikidata Walkabout - a drill-down and query interface to Wikibase sites; powered by Anvesha - a JavaScript library. Video presentation
Codex, the Design System for Wikimedia[edit | edit source]
The Wikimedia Codex design system is analogous to Google's Material Design, Shopify's Polaris, or IBM's Carbon
Codex leverages Vue.js See mw:Codex for details about using the system and it's relationship to prior efforts like MediaWiki UI (deprecated) or OOUI
References[edit source]
- ↑ by Ladsgroup
- ↑ See Simon's https://github.com/General-Process-Ontology/ontology
- ↑ This was in 2022, so before the new version. The project was shown in the presentation at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MZlk5Gzy0tc&t=1564s
- ↑ The dynamic "slide format" of page content is also impressive.