Difference between revisions of "TLS"
(Add service section) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Instantly check your site's security grade at https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html (you can also append the domain name like so: ?d=equality-tech.com) | Instantly check your site's security grade at https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html (you can also append the domain name like so: ?d=equality-tech.com) | ||
| − | == | + | == Let's Encrypt == |
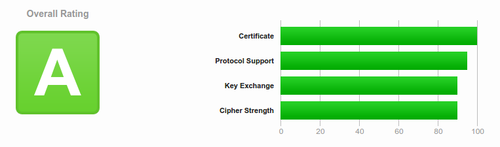
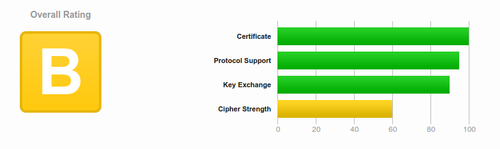
| − | + | We used to run certificates from StartSSL because they offer free one-year certificates. However, today we upgraded to using 'LetsEncrypt' and our certificates are both more secure and easier to manage. Instead of a "B" grade, we now have "A" grade security. | |
| + | [[File:AGrade.png|left|500px]] [[File:BGrade.png|right|500px]] | ||
| − | + | '''Certbot''' ([https://github.com/certbot/certbot code]) is a fully-featured, extensible client for the Let's Encrypt CA (or any other CA that speaks the ACME protocol) that can automate the tasks of obtaining certificates and configuring web servers to use them. This client runs on Unix-based operating systems. It '''requires''' root access and is '''beta''' software. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Until May 2016, Certbot was named simply <code>letsencrypt</code> or <code>letsencrypt-auto</code>, depending on install method. Instructions on the Internet, and some pieces of the software, may still refer to this older name. | |
| − | <code> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [https://certbot.eff.org/#pip-apache Certbot website] at EFF.org (the Electronic Frontier Foundation). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Service == | |
| − | + | Using our [[Ansible]] role, we can install the certbot client. Then we can install as many certificates as needed; plus setup an automated job which will renew them every 90 days. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Using [[ | ||
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
# [[wp:Transport Layer Security|Transport Layer Security]] | # [[wp:Transport Layer Security|Transport Layer Security]] | ||
| + | # https://letsencrypt.org/getinvolved/ Get Involved with Lets Encrypt | ||
| + | ## https://letsencrypt.org/getting-started/ Getting Started | ||
| + | ## https://github.com/letsencrypt/letsencrypt Code on GitHub | ||
| + | ## https://letsencrypt.readthedocs.org/en/latest/ Docs | ||
# https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS | # https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS | ||
# https://security.stackexchange.com/ | # https://security.stackexchange.com/ | ||
# [https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ssl/ Apache docs] | # [https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ssl/ Apache docs] | ||
# [https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/certificates-and-security.html Ubuntu Server Guide - Certificates and Security] | # [https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/certificates-and-security.html Ubuntu Server Guide - Certificates and Security] | ||
| − | # [https:// | + | # [https://github.com/jaywink/ansible-letsencrypt Ansible role for LetsEncrypt] |
[[Category:Security]] | [[Category:Security]] | ||
[[Category:System Administration]] | [[Category:System Administration]] | ||
Revision as of 13:50, 24 August 2016
Transport Layer Security[edit | edit source]
This page is mainly about adding Transport Layer Security TLS (also commonly referred to by it's predecessor 'Secure Sockets Layer or SSL') for your web servers such as Apache or nginx.
If you have a website or other online resources, you should be running them on a Secure webserver. If you need help, call eQuality Technology. We can secure your site very quickly and very cost-effectively, using the highest grade security measures.
Security Check[edit | edit source]
Instantly check your site's security grade at https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html (you can also append the domain name like so: ?d=equality-tech.com)
Let's Encrypt[edit | edit source]
We used to run certificates from StartSSL because they offer free one-year certificates. However, today we upgraded to using 'LetsEncrypt' and our certificates are both more secure and easier to manage. Instead of a "B" grade, we now have "A" grade security.
Certbot (code) is a fully-featured, extensible client for the Let's Encrypt CA (or any other CA that speaks the ACME protocol) that can automate the tasks of obtaining certificates and configuring web servers to use them. This client runs on Unix-based operating systems. It requires root access and is beta software.
Until May 2016, Certbot was named simply letsencrypt or letsencrypt-auto, depending on install method. Instructions on the Internet, and some pieces of the software, may still refer to this older name.
Certbot website at EFF.org (the Electronic Frontier Foundation).
Service[edit | edit source]
Using our Ansible role, we can install the certbot client. Then we can install as many certificates as needed; plus setup an automated job which will renew them every 90 days.
Resources[edit | edit source]
- Transport Layer Security
- https://letsencrypt.org/getinvolved/ Get Involved with Lets Encrypt
- https://letsencrypt.org/getting-started/ Getting Started
- https://github.com/letsencrypt/letsencrypt Code on GitHub
- https://letsencrypt.readthedocs.org/en/latest/ Docs
- https://wiki.mozilla.org/Security/Server_Side_TLS
- https://security.stackexchange.com/
- Apache docs
- Ubuntu Server Guide - Certificates and Security
- Ansible role for LetsEncrypt