Semantic MediaWiki
Semantic MediaWiki is one of the largest, and most complex extensions to MediaWiki - and also an indespensible one for enterprise use. The features it provides are partly described on the Metadata page.
This page exists to dive deeper into particulars.
SMWCon 2023
The 3-day program was fantastic!
One major advancement was the fact that Bernard Krabina opened ties with Open Collective so that individuals and organizations can donate money to the project.
Task tracking
HalloWelt! combines four extensions they created to make useful task tracking in (Semantic) MediaWiki
- Extension:SimpleTasks Tasks are checklist items that can be checked on or off to indicate if the task is open or completed.
- Extension:Checklists Make lists of checkboxes.
- Extension:DateTimeTools Provides date tools in VisualEditor.
- Extension:AtMentions Easily mention a user, with notification
Miriam Schlindwein presented how it's possible to create tasks, assign them to someone, add due dates and how they can be controlled
Realtime integrations with GitLab
Fixing Wikidata
Yaron Koren gave a great presentation (slides) called Enhanced Wikibase on how Wikibase (and therefore Wikidata) are missing features. He showed how he implemented these missing features in a series of developments. One is showcased at Wikidata Walkabout - a drill-down and query interface to Wikibase sites; powered by Anvesha - a JavaScript library. Video presentation
Natural Language Queries to Wikidata: A Naive Prototype
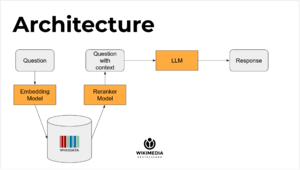
Robert Timms - Sr. Software Engineer Wikibase Suite, Wikimedia Deutschland gave a talk (code slides try it) about querying Wikibase with an LLM. Slides 9-22 go from the application architecture to the 'tada' moment.
Not the goal of the talk, but he revealed some of the key drawbacks of using "AI" in the first place:
- Outdated information
- Prone to hallucinations
- No sources (AI doesn't tell you how or why it claims to be authoritative.)
This is supposed to be addressed in part by using the RAG technique.
| The 'gpt' in ChatGPT stands for "Generative Pre-trained Transformer" - or a fancy way to say "guess". The artificial intelligence of large language model GPTs guess what you would say next based on the prompt given and the dataset they are trained on. In OpenAI's own words: "Generative AI models formulate responses by matching patterns or words, while RAG systems retrieve data based on similarity of meaning or semantic searches." |